Reading Time: 12 minutes | Last Updated: November 11, 2025
Introduction: AI Just Evolved from Tool to Coworker
For the past two years, we’ve been amazed by ChatGPT’s ability to answer questions and write content. But here’s the thing: ChatGPT is still fundamentally reactive. You ask, it responds. You prompt, it generates. It’s brilliant, but it’s always waiting for your instructions.
AI agents are different. They don’t just respond they act. They don’t just answer they plan, execute, and learn. They’re the difference between having a calculator and having an assistant who can solve the entire math problem for you, showing their work and double-checking the answer.
According to Deloitte’s 2025 AI Predictions Report, we’re witnessing 70% growth in autonomous system deployment by 2026. Gartner calls 2025 the pivotal year for agentic AI adoption. Industry analysts predict the autonomous AI agents market will reach $15 billion by 2027.
Why does this matter to you?
Because AI agents are about to change how we work, create, and solve problems. Whether you’re a marketing manager trying to automate campaigns, a small business owner looking to scale, or simply someone trying to understand where AI is headed, understanding agents is no longer optional.
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand exactly what AI agents are, how they differ from chatbots, what makes them “agentic,” and whether they’re right for your needs.
In short: AI agents also known as autonomous AI systems or agentic AI are the next evolution of artificial intelligence. They act independently to plan, execute, and learn toward specific goals, moving beyond traditional chatbots or assistants.
Let’s dive in.

What Are AI Agents? (The Simple Definition)
An AI agent is an autonomous system that perceives its environment, makes decisions, and takes actions to achieve specific goals without requiring constant human instruction for every step.
Put simply, an AI agent is an intelligent software entity that takes initiative. Unlike chatbots, which wait for your prompts, AI agents proactively pursue objectives, gather data, and deliver outcomes. This proactive behavior is what defines agentic AI.
Let’s break that down:
- Autonomous: It can work independently once given a goal
- Perceives: It gathers and understands information from its environment
- Decides: It reasons about what to do next
- Acts: It executes tasks using available tools
- Goal-oriented: It works toward specific objectives
The Factory Worker Analogy
Think of AI agents like workers in a factory:
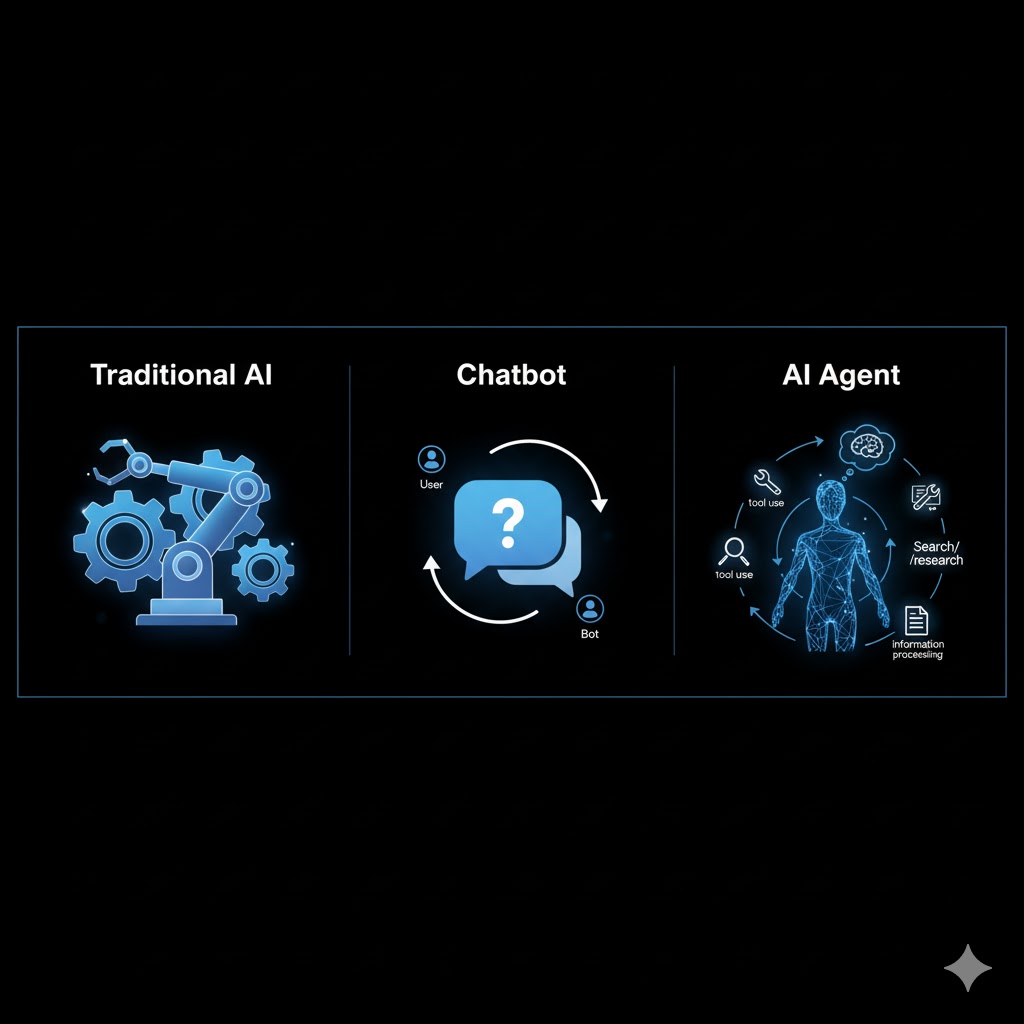
Traditional AI is like a machine on an assembly line. It performs one specific task perfectly, over and over. It’s fast and reliable, but it can’t adapt or make decisions. If something changes, it breaks down.
Chatbots (like basic ChatGPT) are like consultants. They’re smart and helpful when you ask them questions. But they don’t do the work they just tell you what to do. You’re still the one executing.
AI Agents are like skilled workers with autonomy. You give them a project goal (“ship 1,000 units by Friday”), and they figure out the steps, use the tools they need, solve problems that come up, and complete the job. They might ask for clarification on big decisions, but they don’t need you watching over their shoulder for every action.
Agents vs. Chatbots vs. Traditional AI: What’s the Difference?
Here’s how they compare:
| Feature | Traditional AI | Chatbots | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interaction Style | Rule-based, predetermined | Reactive prompt-response | Autonomous decision-making |
| Workflow | Fixed procedures | Single-step responses | Multi-step planning & execution |
| Environment Awareness | Fixed inputs only | Limited context (conversation) | Perceives and adapts dynamically |
| Autonomy Level | Low (follows programmed rules) | Medium (responds to prompts) | High (self-directed toward goals) |
| Tools & Memory | Simple, limited | Rare or basic | Complex persistent memory, multiple tools |
| Example | Spam filter | ChatGPT answering questions | AutoGPT building a website |
These distinctions are critical for understanding the rise of agentic AI systems in 2025. Tools that blend autonomy, reasoning, and real-time decision-making to achieve measurable goals.
The Critical Difference: Agency
The key word is agency: the ability to act independently toward a goal.
A chatbot waits for your next instruction. An agent takes initiative to accomplish the goal you’ve given it.
Example:
You say: “I need to understand our competitor’s pricing strategy.”
Chatbot response: “I can help you analyze competitor pricing. Please provide me with the competitor names and their pricing information, and I’ll create an analysis for you.”
Agent response: “I’ll research that for you. I’m going to search for your top 3 competitors, extract their pricing from their websites, compare it to your current pricing, and generate a strategic recommendation report. This should take about 3 minutes. Should I proceed?”
Then the agent actually does all of that searching, extracting data, analyzing, and delivering the report.
See the difference? One tells you how. The other actually does it.
The Five Core Capabilities That Make Agents “Agentic”
What gives agents their autonomy? Five fundamental capabilities working together:
These are the essential building blocks of every autonomous AI agent, from perception to decision-making—that enable modern agentic AI applications.
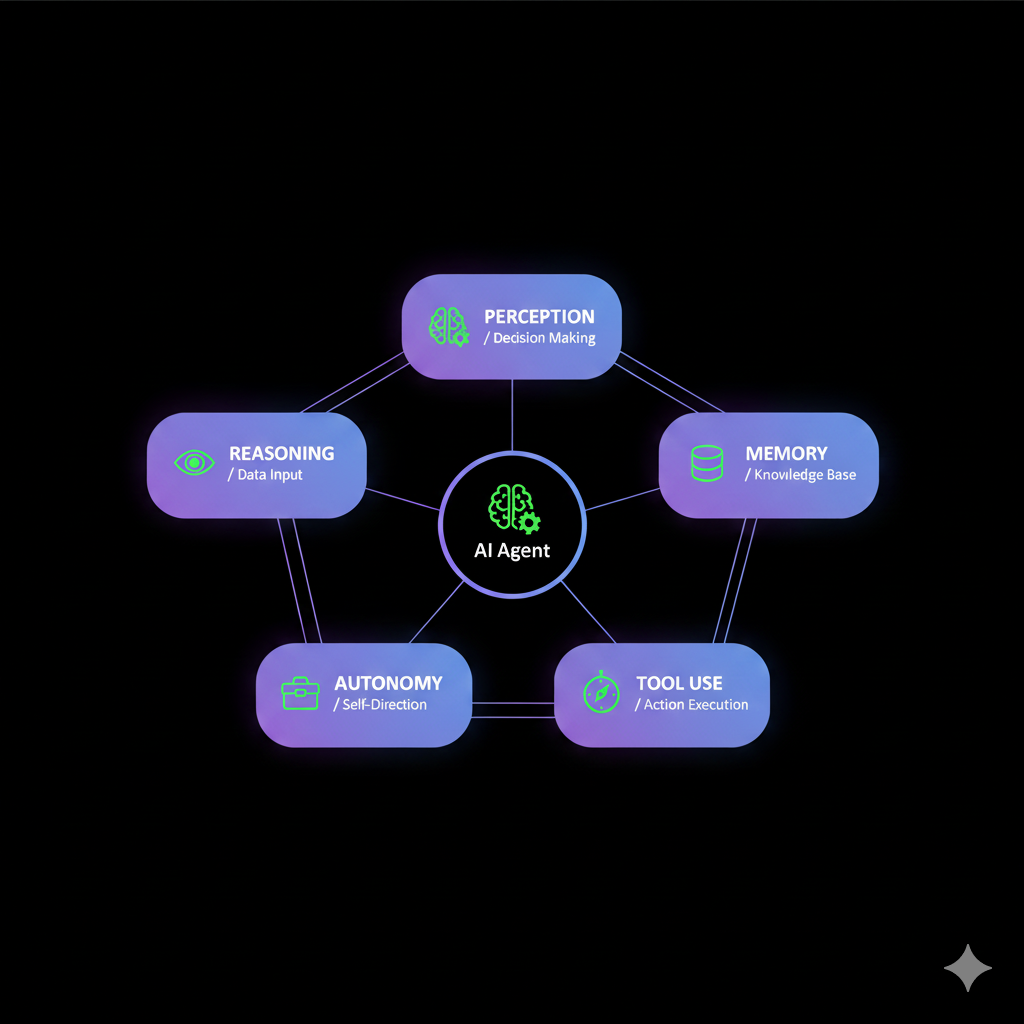
1. Perception: Understanding the Environment
What it is: The ability to gather and interpret information from various sources, documents, databases, APIs, user inputs, or live data streams.
How it works: Agents process multiple data types (text, images, structured data) to build a picture of their current situation. This isn’t just reading, it’s understanding context, relationships, and relevance.
Real-world example: A customer service agent perceives:
- The incoming email’s content
- The customer’s tone (frustrated, confused, satisfied)
- Past interaction history from the CRM
- Current order status from the database
- Company policy documents
- Time-sensitive factors (holiday season, shipping delays)
It synthesizes all this to understand: “This is an angry customer whose order is delayed, and it’s the third inquiry.”
2. Reasoning & Planning: Breaking Down Complex Goals
What it is: The cognitive ability to decompose a high-level goal into a sequence of actionable steps, anticipate challenges, and create strategies.
How it works: Using chain-of-thought reasoning, agents think through problems step-by-step. They don’t just react, they strategize.
Real-world example: A marketing agent given the goal “launch a product announcement campaign” reasons:
Goal: Launch product announcement campaign
↓
Step 1: Research target audience demographics
Step 2: Identify top 3 messaging angles based on research
Step 3: Create content variations for each angle
Step 4: Schedule posts across 3 platforms (LinkedIn, Twitter, email)
Step 5: Set up performance tracking
Step 6: Monitor first 24 hours and adjust underperforming content
The agent didn’t just execute a template, it created a plan based on the specific product, audience, and goals.
Key insight: According to research from Google Brain (2022), chain-of-thought prompting improves AI reasoning accuracy by 30-40% on complex tasks. Agents use this capability continuously.
3. Memory: Learning from Experience
AI agents have two types of memory that work together:
Short-term memory (Working Memory):
- Maintains context within a single task or conversation
- Tracks what’s been done and what comes next
- Duration: Current session or workflow
Example: Remembering the previous 10 steps in a research task, so it doesn’t duplicate work or lose the thread.
Long-term memory (Knowledge Base):
- Stores information across sessions
- Learns user preferences, past decisions, and outcomes
- Duration: Persistent across weeks, months, or indefinitely
Example: A sales agent remembering that Client X prefers email over phone calls, responds better to data-driven pitches, and has a budget cycle ending in Q4.
Why this matters: Memory transforms an agent from a one-off tool into a genuine assistant that gets smarter over time. It’s the difference between explaining your preferences every single time versus having an agent that “just knows” how you work.
Technical note: Long-term memory typically uses vector databases to store and retrieve relevant information based on semantic similarity: a technique covered in Anthropic’s Claude guide to Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
4. Tool Use: Accessing External Capabilities
What it is: The ability to use external tools, APIs, and services to accomplish tasks that the base AI model can’t do alone.
Agents aren’t limited to generating text. They can:
- Search the web for current information
- Query databases for specific data
- Send emails or Slack messages
- Execute code and run calculations
- Create files and edit documents
- Call APIs to integrate with other software
- Control other AI models (text-to-image, speech-to-text)
Real-world example: A research agent asked to “analyze our competitor’s pricing strategy” might:
- Use web search to find competitor websites
- Use web scraping to extract pricing tables
- Use a calculator to compute price differences
- Use spreadsheet tools to organize data
- Use GPT-4 to analyze trends and write a summary report
All autonomously, without you manually performing each step.
5. Autonomy: Self-Directed Execution
What it is: The ability to work toward goals without constant human oversight is the defining characteristic of agents.
The autonomy spectrum:
Full Human Control ←――――――――――――→ Full Autonomy
[Human does everything] → [Human reviews each step] → [Human reviews final output] → [Agent works independently]
Most production agents operate in the “autonomous with human oversight” range, they execute independently but escalate critical decisions.
Example decision logic:
- ✅ Auto-approve: Routine tasks with low risk (scheduling social posts)
- ⚠️ Flag for review: Medium-stakes decisions (choosing between 3 campaign strategies)
- 🛑 Require approval: High-stakes actions (spending >$5,000, legal decisions)
The guardrails question: Autonomy doesn’t mean reckless. Well-designed agents have:
- Scope limitations: “You can only edit content, not delete”
- Budget caps: “Maximum $500 per transaction”
- Human-in-the-loop checkpoints: “Confirm before sending to >100 people”
- Rollback capabilities: Undo mistakes
Critical insight: According to Stanford’s AI Safety and Ethics Group, the most successful agent deployments balance autonomy with appropriate guardrails. Complete autonomy is rarely the goal, effective autonomy is.
Quick Example: Watch an Agent in Action
Let’s see these five capabilities work together in a simple scenario:
Your goal: “Find three gift ideas for my colleague who loves hiking, under $50 each.”
What the agent does:
1. Perception (Understanding):
- Recognizes: Need product recommendations
- Key criteria: Hiking-related, under $50, gift-appropriate
- Context: This is for a colleague (professional relationship)
2. Reasoning (Planning):
Plan:
Step 1: Search for hiking gift ideas
Step 2: Filter by price (<$50)
Step 3: Evaluate appropriateness for colleague
Step 4: Select 3 diverse options (not all the same type)
Step 5: Present with rationale
3. Memory (Context):
- Remembers you previously asked about outdoor gifts (if applicable)
- Stores hiking interest for future gift recommendations
4. Tool Use (Execution):
- Action 1: Web search for “best hiking gifts under $50”
- Action 2: Check current prices on Amazon/REI
- Action 3: Read product reviews
- Action 4: Filter results
5. Autonomy (Self-Direction):
- Completes all steps without asking for permission at each stage
- Only returns when it has the final answer
Final Output:
I found three great hiking gift options for your colleague:
1. **Portable Water Filter ($35)** - Practical for any hiker, highly rated
2. **Hiking Trail Guidebook - Pacific Northwest ($24)** - Local relevance, inspires future adventures
3. **Packable Daypack ($42)** - Versatile, good quality brand
All are professional-appropriate and under $50. Would you like links to purchase any of these?
Total time: 2 minutes (vs. 20+ minutes if you did the research manually)
Real-World Examples: Where AI Agents Are Working Today
1. Customer Service
The problem: Support teams drowning in repetitive tickets, customers waiting hours or days for responses.
The agent solution: Autonomous customer service agents that read tickets, search knowledge bases, resolve routine issues automatically, and escalate complex cases with full context.
Impact:
- 60-70% of tier-1 tickets resolved without human intervention
- Response time: Under 2 minutes (vs. 4-24 hours)
- Support agents freed for complex, high-value interactions
Example tasks:
- “Where is my order?” → Check shipping database, provide tracking
- “I need to return this” → Initiate return, generate label
- “Reset my password” → Verify identity, send reset link
2. Research & Analysis
The problem: Researchers spend days gathering information from multiple sources and synthesizing insights.
The agent solution: Research agents that search across databases, extract relevant information, cross-reference facts, identify patterns, and generate structured reports with citations.
Impact:
- JPMorgan Chase COiN: AI agent automates legal document review, completing 360,000 hours of work in seconds (JPMorgan Annual Report, 2023)
- Research that took weeks now takes hours
- More comprehensive analysis (processes far more sources)
3. Business Operations
The problem: Repetitive workflows eat up employee time, data entry, report generation, email responses, scheduling and are always prone to lack of attention errors.
The agent solution: Operations agents that process documents, extract and validate data, update multiple systems, generate reports, and handle approvals.
Impact:
- 70-80% reduction in manual data entry
- Fewer errors (AI more consistent on repetitive tasks)
- Employees freed for strategic work
Example: Accounts payable agent
- Receives invoice email
- Extracts vendor, amount, due date
- Verifies against purchase order
- Routes to appropriate approver
- Schedules payment
- Updates accounting system
4. Content Creation & Marketing
The problem: Marketing teams need to produce massive amounts of content across multiple channels, constantly.
The agent solution: Content agents that research topics, create drafts, optimize for SEO, generate variations for different platforms, and schedule distribution.
Impact:
- 10-20 hours saved per week on content production
- Consistent brand voice across channels
- Faster response to trends and opportunities
5. Software Development
The problem: Developers spend 60-70% of time on repetitive tasks, boilerplate code, debugging, tests, documentation.
The agent solution: Coding agents that generate code from descriptions, write tests automatically, debug errors, and update documentation.
Impact:
- GitHub Copilot: 75% of developers report increased productivity (GitHub User Survey, 2024)
- 40% reduction in time-to-feature completion
In summary, AI agents are already transforming industries through automation, autonomy, and adaptability. Whether in research, customer support, or operations, autonomous AI systems are redefining productivity and decision-making across sectors.
Common Misconceptions About AI Agents
Let’s clear up some myths:
❌ Myth 1: “Agents will replace all workers”
✅ Reality: Agents augment human capabilities, they don’t replace human judgment.
According to McKinsey’s AI Survey (2024), the most successful AI deployments involve human-AI collaboration:
- Agents handle repetitive, data-heavy tasks
- Humans focus on strategy, creativity, and complex decisions
- Productivity increases 2-5x when roles are properly divided
Jobs are evolving, not disappearing. Roles shift toward supervision, training, and strategic use of AI.
❌ Myth 2: “Agents are just better chatbots”
✅ Reality: They’re fundamentally different systems.
A chatbot answers “How do I schedule a meeting?” An agent actually schedules the meeting.
The key difference: Autonomy and goal-oriented behavior.
❌ Myth 3: “Agents are fully autonomous and need no oversight”
✅ Reality: Most production agents require guardrails and human oversight for critical decisions.
Best practice: Start with high oversight, gradually increase autonomy as trust is earned through consistent performance.
❌ Myth 4: “You need to be technical to use agents”
✅ Reality: No-code platforms are making agents accessible to everyone.
Current options:
- No-code: ChatGPT Custom GPTs, Microsoft Copilot Studio
- Low-code: Zapier + AI, Make.com with agent features
- Full code: LangChain, AutoGPT for custom development
By 2026, Gartner predicts 60% of agent deployments will use no-code or low-code platforms.
❌ Myth 5: “Agents are hallucination-free”
✅ Reality: Agents can still hallucinate, but tool use and verification significantly reduce the problem.
How agents mitigate hallucinations:
- Tool use: Search for real information instead of guessing
- Citations: Show sources for verification
- Verification loops: Cross-check their own outputs
- Explicit uncertainty: Say “I don’t know” when unsure
Research shows RAG-based agents have 52% fewer hallucinations compared to standalone LLMs, but they’re not perfect.
Best practice: Human review for high-stakes decisions, always verify critical information.
Should You Use AI Agents? A Simple Decision Framework
Not every problem needs an agent. Here’s how to decide:
✅ Good Fit for Agents
Your task is a good candidate if it:
- Is repetitive with clear success criteria
- Requires multiple steps or data sources
- Involves information gathering and synthesis
- Would benefit from 24/7 availability
- Has clear inputs and outputs
- Currently takes significant human time
Examples:
- Weekly competitive intelligence reports
- Customer FAQ responses
- Data extraction from documents
- Content repurposing across platforms
- Meeting notes and summaries
If you’re researching which agentic AI platform to start with, explore our AI Agent Tools Directory to compare no-code and low-code options, pricing, and reviews.
❌ Poor Fit for Agents
Avoid agents for tasks that:
- Require pure creativity with no structure
- Involve high-stakes decisions with no room for error
- Need deep human empathy or emotional intelligence
- Change constantly with no predictable patterns
- Require physical presence or manipulation
Examples:
- Strategic business pivots
- Sensitive HR conversations
- Creative art direction
- Crisis management
- Safety-critical operations
Questions to Ask
Before building an agent, clarify:
- What’s the specific goal?
- Vague: “Help with marketing”
- Specific: “Research competitors, draft weekly newsletter, schedule social posts”
- What’s the success metric?
- Time saved?
- Quality improvement?
- Cost reduction?
- What are the risks if it fails?
- Financial loss?
- Reputation damage?
- Customer impact?
- What’s the appropriate autonomy level?
- Fully autonomous?
- Review before action?
- Approval required?
Getting Started: Your First AI Agent
Ready to try agents? Here’s the simplest path:
Step 1: Start Small
Recommended first projects:
- Personal research assistant: Gather information on topics you care about
- Content repurposer: Turn one blog post into social media threads
- Email summarizer: Daily digest of important emails
- Meeting note-taker: Transcribe and summarize calls
Why these? Low risk, clear value, easy to evaluate.
Step 2: Choose a No-Code Platform
Best AI Agent Platforms in 2025 (No-Code and Low-Code Options)
Looking for the best autonomous AI agents to try? Here are popular beginner-friendly platforms:
- Claude (Anthropic) – Free, Pro $20/month
- Best for: Reliable, safe, and high-performing agents for customer support and automation
- Capabilities: Runs complex knowledge tasks, supports custom tools, high limits on context and file handling
- Microsoft Copilot (Microsoft 365)
- Best for: If you already use Microsoft tools and want seamless workflow integration
- Capabilities: Email, calendar, documents, Teams integration, code and data automation
- n8n AI Agents – Free, Pro starts $20/month
- Best for: Flexible, visual automation and custom AI-driven workflows with 500+ integrations
- Capabilities: Visual workflow builder, integrates GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, native app connections, reasoning engine, multi-language support, file/data processing, self-hosting option
- Make.com AI Agents – Free, Pro starts $16/month
- Best for: Modular task automation across 3000+ apps with customizable goal-driven AI agents
- Capabilities: Adaptive AI agents using LLMs, scenario-driven automation, natural language prompts, deep workflow customization, accessible interfaces (Slack, web, etc.), over 30,000 actions/integrations
- ChatGPT Custom GPTs (OpenAI) – $20/month
- Best for: Simple conversational agents, knowledge work, and flexible automation
- Capabilities: File upload, web search, code execution, plugin/app ecosystem, integrations with Microsoft and Zapier
- LangChain – Free/Open Source
- Best for: Developers building advanced, custom autonomous AI workflows
- Capabilities: Modular architecture, agent memory, external tool calls, data processing, integrates with leading LLMs
- AgentGPT – Free, Pro $15/month
- Best for: Browser-based autonomous agents for quick task automation
- Capabilities: Goal-driven agents that break tasks into steps, write, research, automate web tasks
Step 3: Define Your Agent
Template to fill out:
AGENT NAME: [e.g., "Weekly Research Assistant"]
GOAL: [e.g., "Research AI industry news every Monday and create a summary report"]
INPUTS: [e.g., "List of sources to check, topics of interest"]
STEPS:
1. [e.g., "Search top 5 AI news sources"]
2. [e.g., "Extract articles from past week"]
3. [e.g., "Summarize key developments"]
4. [e.g., "Identify trends"]
5. [e.g., "Generate formatted report"]
OUTPUT: [e.g., "Email with 5-bullet summary + links"]
AUTONOMY: [e.g., "Run automatically every Monday, no approval needed"]
Step 4: Test & Iterate
- Run manually first: Guide it through the process
- Review outputs: Check for accuracy and usefulness
- Refine instructions: Based on what goes wrong
- Gradually automate: Once you trust the outputs
Step 5: Measure Success
Track:
- Time saved per week
- Quality of outputs (subjective rating)
- Errors requiring correction
- ROI (value of time saved vs. cost of agent)
Example: If your agent saves 5 hours/week and your time is worth $50/hour, that’s $1,000/month in value. Even at $100/month in costs, that’s 10x ROI.
What’s Next: Continue Your AI Agent Journey
Congratulations! You now understand what AI agents are, how they work, and whether they’re right for you.
Want to Go Deeper?
We will update this section to add future articles and guides
→ Explore Our AI Agent Tools Directory
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Agents
Q1. What is an AI agent in simple terms?
An AI agent is an autonomous AI system that can make decisions and take actions toward a goal without step-by-step human control.
Q2. How is an AI agent different from a chatbot?
Chatbots are reactive: they answer questions when prompted. AI agents are proactive: they plan and execute tasks to achieve goals.
Q3. What are some real-world examples of AI agents in 2025?
Customer support bots, research assistants, coding agents, and workflow automation tools like AutoGPT, Copilot, and ChatGPT Custom GPTs.
Q4. Do I need to code to use AI agents?
No. Many no-code platforms like ChatGPT Custom GPTs, Microsoft Copilot, Make.com and Zapier AI let you create functional agents without technical skills.
Q5. What are the best AI agent platforms to try?
Top-rated options in 2025 include Claude (Anthropic), Zapier AI, n8n AI Agents, Make.com AI Agents, OpenAI GPTs and Microsoft Copilot, each with varying autonomy and integrations.
Key Takeaways
Remember these essentials about AI agents:
- Agents ≠ Chatbots: Agents are autonomous and goal-oriented; chatbots are reactive
- Five Core Capabilities: Perception, reasoning, memory, tool use, autonomy
- Augmentation, Not Replacement: Agents handle repetitive tasks, humans do strategy
- Guardrails Required: Most agents need oversight for high-stakes decisions
- No-Code Options Available: You don’t need programming skills to start
- Start Small: Pilot with low-risk projects, supervised deployment
- The Market Is Growing: 82% of organizations will deploy agents by 2026 (Capgemini)
The bottom line: AI agents represent a fundamental shift from “AI as tool” to “AI as coworker.” Organizations that master agentic AI will have significant competitive advantages.
The future of work isn’t humans OR AI. It’s humans WITH AI agents.
Found this helpful? Share it with your team, bookmark for reference, and subscribe to our newsletter for weekly AI insights.
Questions about AI agents? Join the discussion in the comments below or explore our community.
Last updated: November 6, 2025 | Written by the Vantaige team | 12 min read
Citations:
- Deloitte AI Trends Report 2024
- Gartner Emerging Tech Hype Cycle 2025
- Google Brain: Chain of Thought Prompting 2022
- JPMorgan Annual Report 2023
- GitHub Copilot User Survey 2024
- Capgemini AI Report 2024
- Stanford AI Safety and Ethics Group
- McKinsey AI Survey 2024
- MarketsandMarkets Report 2024
